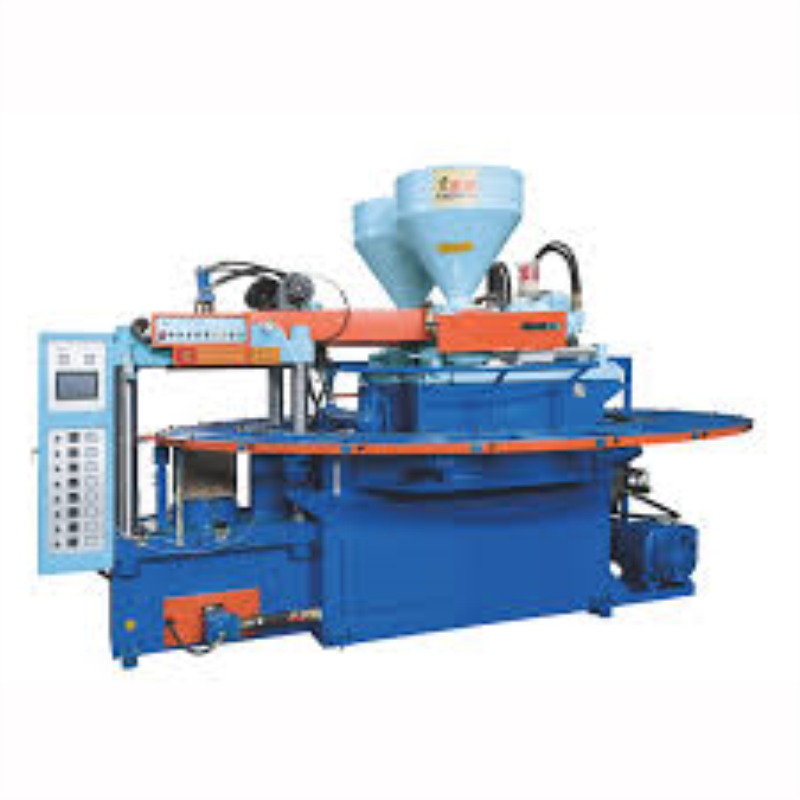
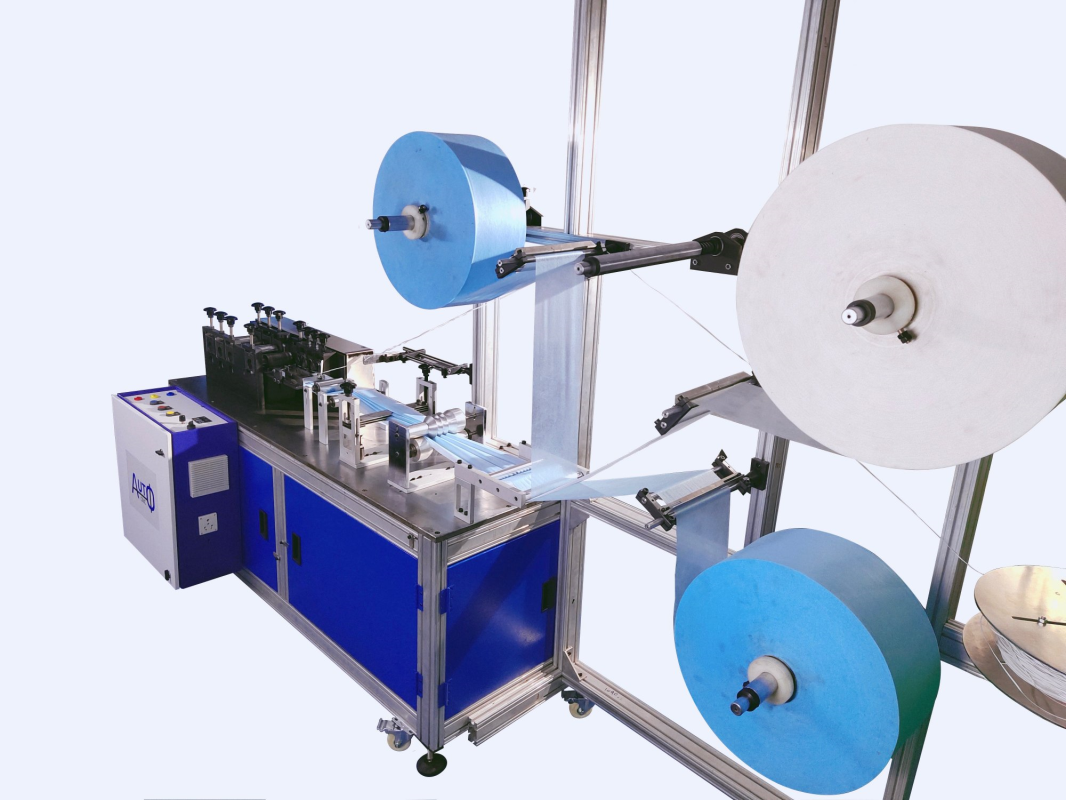
Tablet Making Machine – Precision Engineering for Efficient Manufacturing
A tablet making machine, also known as a tablet press or tablet manufacturing machine, is a specialized piece of equipment used for the automated production of pharmaceutical tablets. These machines are crucial in the pharmaceutical industry for efficiently and accurately producing tablets, which are solid dosage forms commonly used for delivering medications and supplements.
Here's a more detailed overview of the components and operation of a tablet making machine.
Components of a Tablet Making Machine
- Hopper:The hopper holds the granulated material or powder that will be compressed into tablets.
- Feeder: The feeder delivers a controlled amount of material from the hopper to the compression area.
- Compression Area: This is where the actual tablet formation occurs. It consists of upper and lower punches that come together to compress the material into tablet form.
- Die Cavity: The die cavity defines the shape and size of the tablet. It's the space into which the material is compressed to create the tablet.
- Compression Mechanism: The compression mechanism brings the upper and lower punches together with a controlled force to compress the material and form the tablet.
- Ejection Mechanism: After compression, an ejection mechanism releases the formed tablet from the die cavity.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Some machines incorporate sensors and systems to inspect the tablets for defects, ensuring uniformity and quality.
- Tablet Coating (Optional): Some tablet making machines also have provisions for tablet coating, which can improve the tablet's appearance, taste, and stability.
Operation
- Material Loading: The granulated material or powder is loaded into the hopper.
- Feeding: The feeder delivers a controlled amount of material to the compression area.
- Compression: The upper and lower punches come together to compress the material into tablet form within the die cavity.
- Ejection: An ejection mechanism releases the formed tablet from the die cavity.
- Quality Control: Sensors and systems inspect the tablets for defects and ensure uniformity and quality.
- Coating (Optional): If the machine has a coating unit, tablets can be coated to improve appearance and other characteristics.
Key Considerations
- Tablet Size and Shape: Different machines are designed to produce tablets of various sizes and shapes.
- Material Type: Tablets can be made from various materials, including pharmaceutical powders, granules, and other ingredients.
- Compression Force: The force applied during compression affects tablet hardness and density.
- Uniformity: Ensuring uniformity in tablet weight, size, and content is critical for consistent dosing.
- Coating Options: Some machines offer options for tablet coating to improve appearance and other properties.
- Quality Control: Maintaining consistent quality is essential for producing reliable and effective tablets.
Tablet making machines are essential tools in the pharmaceutical industry, allowing for precise and efficient production of medications and supplements in tablet form. These machines contribute to ensuring accurate dosing, easy administration, and controlled release of pharmaceutical substances.
Homeopathy Medicine Making medicine
Homeopathy is based on the principles of dilution and succussion (vigorous shaking) to create highly diluted remedies that are believed to have healing properties. However, the extreme dilutions used in homeopathy often result in solutions where the original substance is no longer present.
Allopathic Medicine Making Machine
In allopathic medicine, medications and treatments are developed through extensive research, clinical trials, and regulatory approval processes. There are pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and medical professionals involved in the discovery, development, and manufacturing of medications and medical devices. The process of creating medications involves.
- Research and Development: Scientists identify potential targets for new medications, conduct laboratory research to develop compounds, and test their effectiveness in treating specific conditions.
- Preclinical Testing: Promising compounds undergo preclinical testing in the laboratory and on animals to assess their safety and effectiveness.
- Clinical Trials: If a compound shows promise in preclinical testing, it progresses to clinical trials, which involve testing on human volunteers. Clinical trials follow a rigorous protocol to gather data on safety, efficacy, and potential side effects.
- Regulatory Approval: After successful clinical trials, pharmaceutical companies submit the data to regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for approval to market the medication.
- Manufacturing: Once approved, the medication is manufactured in controlled facilities following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure quality, consistency, and safety.
- Distribution and Prescription: The medication is then distributed to healthcare providers who can prescribe it to patients based on their medical needs.
- Patient Monitoring: Patients taking allopathic medications are typically monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure the treatment's effectiveness and address any potential side effects.
Veterinary Medicine Making Machine
In veterinary medicine, medications are often administered to animals to treat various health conditions. These medications can be produced in various forms, including tablets, liquids, injections, and more. Compounding pharmacies or veterinary pharmaceutical companies may use specialized equipment to manufacture medications for animals, including birds.